Across all ages, diarrheal disease causes more illnesses than any other ailment and is second only to pneumonia as the largest killer of children under five years. Children who survive an episode of diarrhea, but experience recurring infections, are more likely to suffer from lifelong cognitive and physical impairments.
The state of the field is changing
Diarrheal disease is preventable and treatable, and more children than ever have these tools within reach. Although this has led to a decline in deaths in recent years, children are still getting sick, facing the long-term consequences of malnutrition and repeated infections.
Importantly, subnational data show that the children at highest risk of diarrhea death or long-term health impacts are in the poorest regions. Diarrhea burden is a manifestation of broader inequity; these children bear the brunt of COVID-19’s cascading impact, including declining immunization rates and strains on already fragile health systems. Gender equity, antibiotic resistance, climate change, conflict, and rapid urbanization exacerbate the risks.

The World Health Organization (WHO) defines diarrhea as the passage of three or more loose or liquid stools per day. Also known as gastroenteritis, diarrheal disease is caused by germs (both viral and bacterial) and parasites that are spread from the waste of an infected person to the mouth of another person through contaminated water, food, objects, or hands. During a diarrhea episode, fluids are depleted. Diarrhea becomes deadly when it results in dehydration that goes untreated. Infants and young children are especially vulnerable to rapid dehydration.
The top six pathogens responsible for diarrhea are:
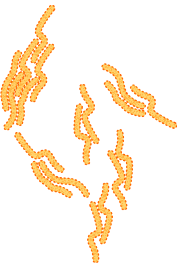
Shigella
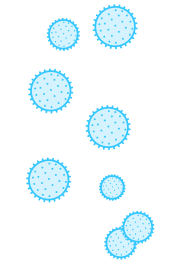
Rotavirus
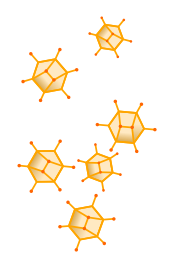
Adenovirus
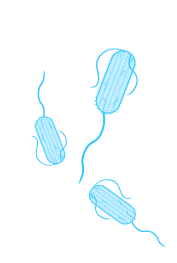
Enterotoxigenic E. coli

Cryptosporidium

Campylobacter
It’s not a hopelessly long list of infections that we can’t do anything about.
- Dr. Eric Houpt, Professor of Infectious Diseases and International Health, University of Virginia
Humanosphere
Who is at risk?
Diarrhea is a threat everywhere, but its frequency and impact are more severe in low-resource settings. Just 15 countries carry 70% of the global diarrheal burden, and progress on tackling this resilient threat is inconsistent, according to the International Vaccine Access Center’s 2023 Progress Report. Whether a child survives a diarrhea infection often depends on where he or she lives and receives treatment. In poorer countries, where access to hospitals or other forms of basic medical care—including intravenous (IV) fluids—may be limited, diarrheal disease can cause death or lasting impairments.
Diarrhea is deadly and dangerous
Deaths from diarrhea disproportionately impact children living in poverty due to:
- Inadequate water supply/unsafe drinking water
- Lack of access to sanitation (the safe disposal of human waste)
- Limited access to soap and water and knowledge of good hygiene practices
- Limited access to vaccines
- Limited access to health care
- Limited knowledge about diarrhea prevention and treatment
Globally, unsafe water and sanitation are the leading risk factors for diarrhea. Infants who are not exclusively breastfed or are malnourished, and immunocompromised young children and adults are also at great risk.
Despite substantial reductions in deaths among children under five years—from more than 1 million to less than 450,000 each year in the last two decades—diarrhea remains one of the deadliest threats young children face. Specifically, it is responsible for about nine percent of all worldwide deaths in young children.
The latest available estimates on diarrheal disease-related deaths are summarized below. Findings across sources are relatively consistent.
| Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Study/Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME)
Latest estimates: 2021, published 2024 | IGME UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation
Latest estimates: 2021, published 2023 |
| Total number <5 deaths
4.7 million | Total number <5 deaths
4.9 million |
| Annual number <5 diarrheal deaths
340,429 | Annual number <5 diarrheal deaths
443,833 |
| Percent of all <5 deaths due to diarrhea
7.3% | Percent of all <5 deaths due to diarrhea
9% |
| Change:
From 1990 to 2021, diarrhea deaths among children under 5 years decreased by 50%. | Change:
From 2000 to 2021, diarrhea deaths among children under 5 years decreased by 63%. |
Recent trends
Diarrhea deaths in children are on the decline. Progress has been faster in some regions and countries than in others. The IHME’s Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study found that, between 1990 and 2021:
- Global life expectancy increased by 6.2 years between 1990 and 2021. This was mainly due to reductions in deaths from enteric infections like diarrheal and typhoid diseases.
- Eastern sub-Saharan Africa experienced the largest increase in life expectancy (which jumped by 10.7 years between 1990 and 2021), primarily due to control of diarrheal diseases in the region.
- The majority of child deaths from diarrhea still occur in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, but in increasingly concentrated areas.
These maps show the burden of diarrhea by geographic area.
Diarrhea deaths by country in 2021
The top 10 countries where the most diarrhea deaths among children occur (measured in deaths per 100,000 people):
NIGERIA
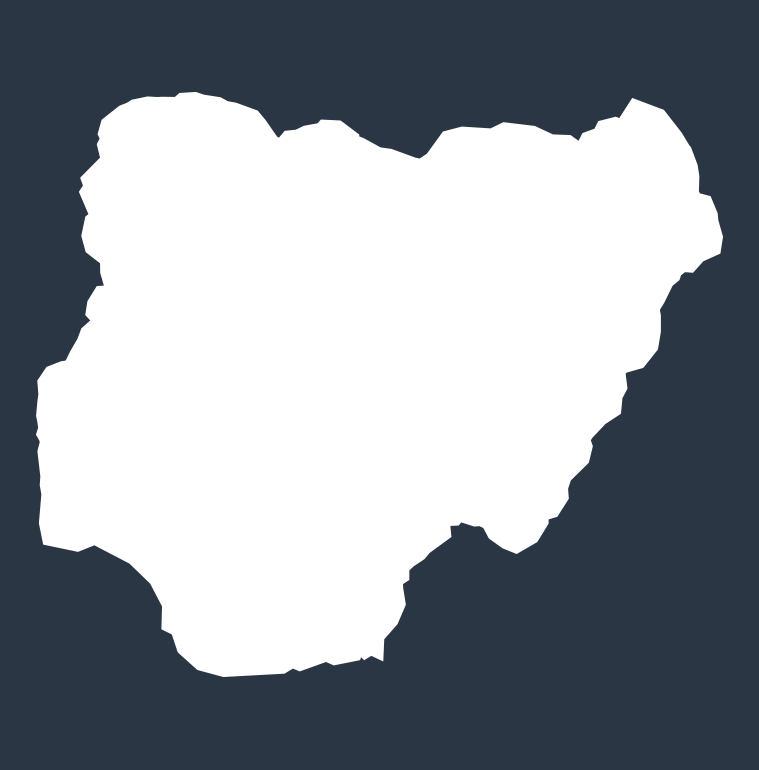

135,857
INDIA
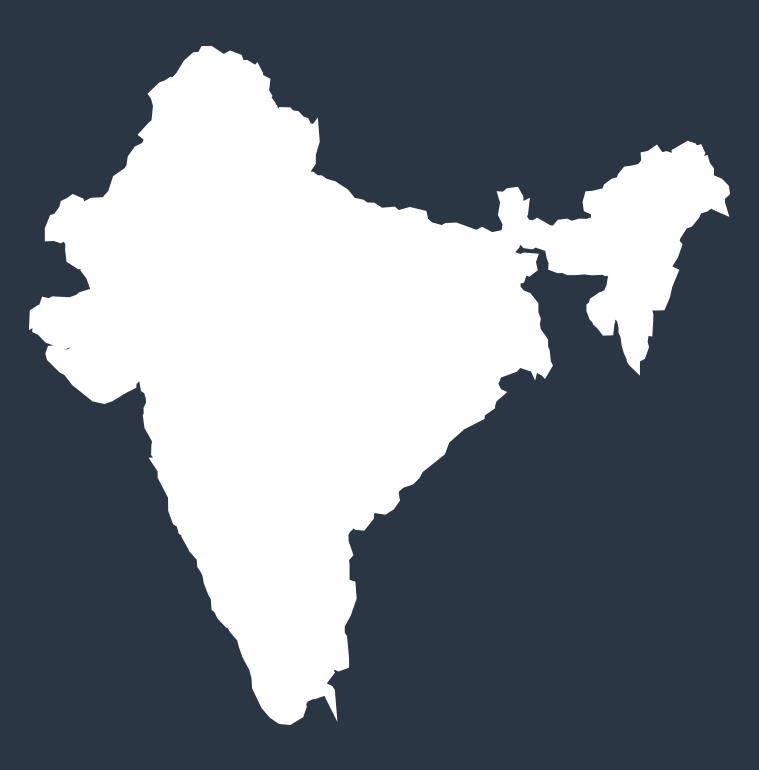
39,863
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO
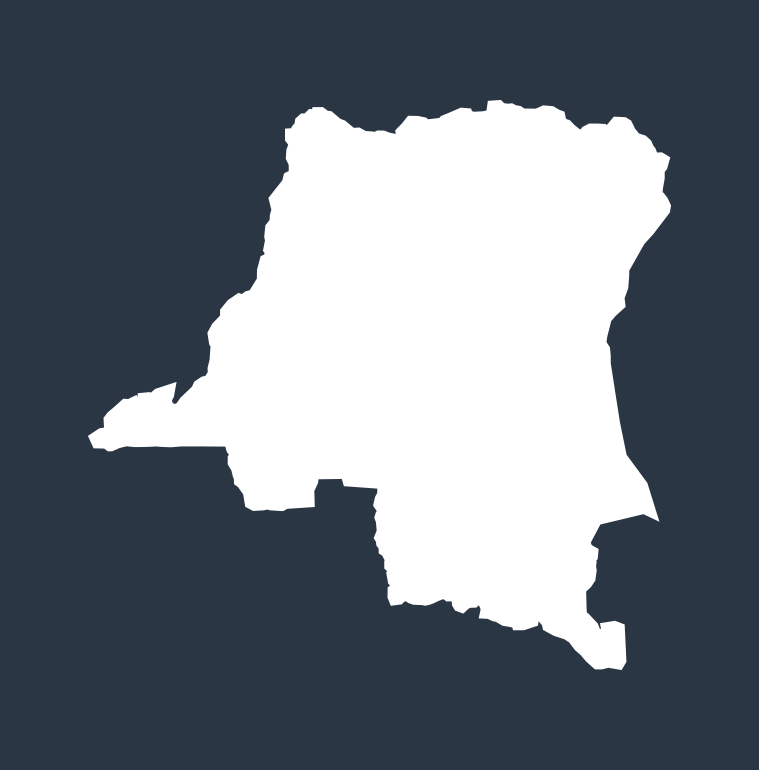
27,466
PAKISTAN
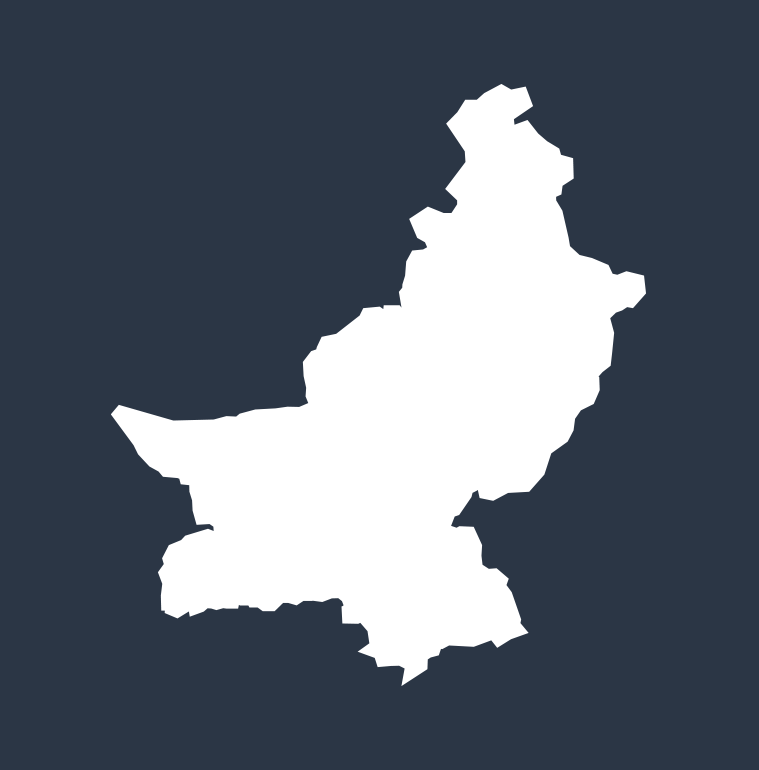
25,791
NIGER
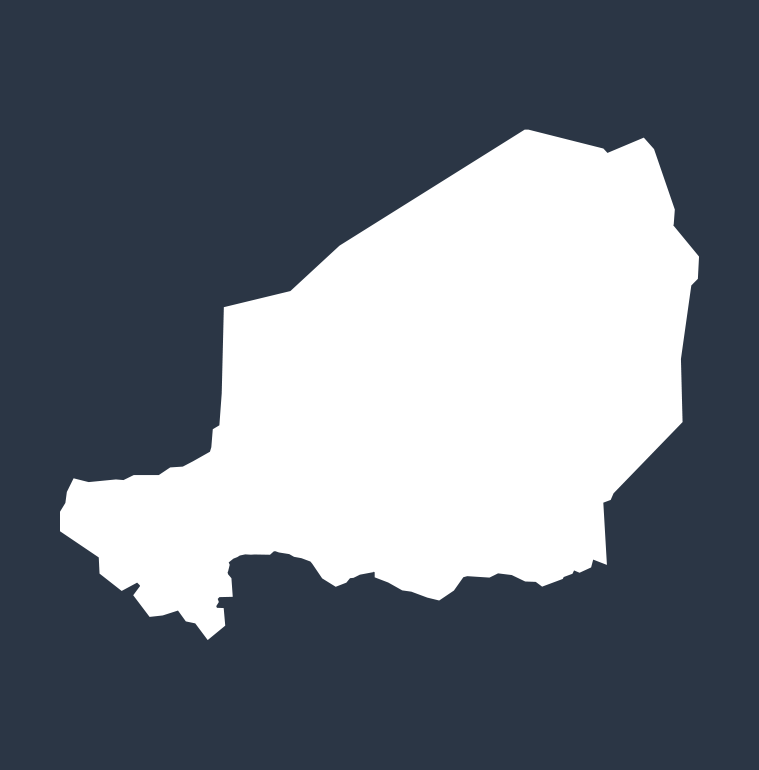
15,936
ETHIOPIA
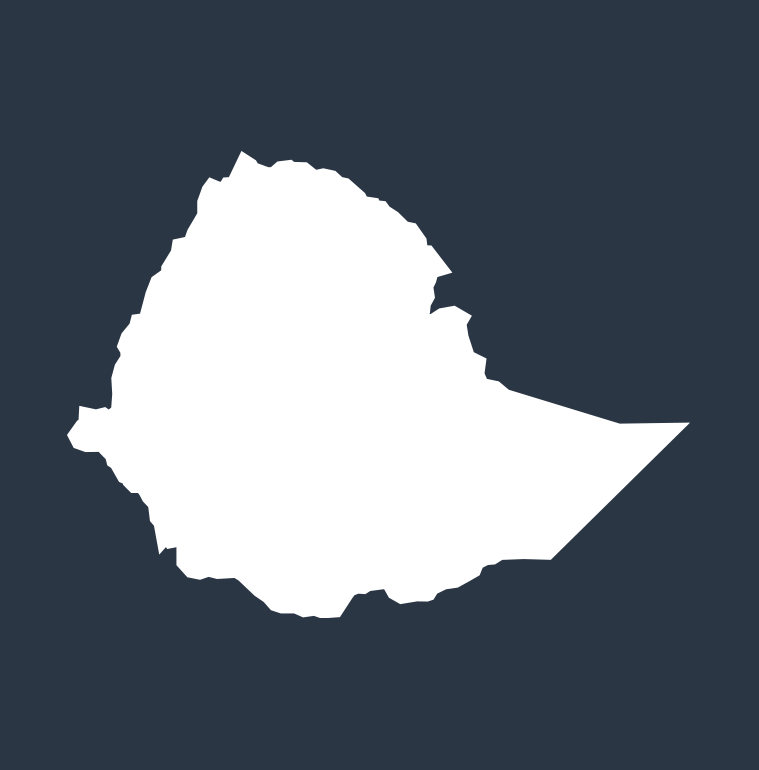

15,273
SOMALIA

11,453
TANZANIA
10,264
ANGOLA
10,251
CHAD
10,228
The United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UN IGME) data demonstrates that there can be significant inequities between countries. For a deeper look at progress, challenges, and opportunities in each high-burden country, check out these Child Health Spotlights from Save the Children and UNICEF.
We can make public health gains when we invest in the right solutions and strategies—and then motivate policymakers to accelerate progress and ‘finish the job.’ Often, the biggest obstacle is people thinking that aid doesn’t pay off. With diarrhea, it has and still can.
- Eileen Quinn, Director, Advocacy and Communications, Center for Vaccine Innovation and Access at PATH
Diarrhea deaths are preventable
Diarrhea can be prevented by:

Vaccines

WASH
Breastfeeding & Nutrition
Diarrhea can be treated by:
ORS & Zinc

Research
Simple and proven solutions can prevent and treat diarrhea. Integrating them together achieves the greatest impact.
Deaths are not the only problem—young children are still getting sick
Diarrhea infections are not declining as fast as the rate of deaths. While diarrhea deaths declined significantly among young children between between 2019 and 2021, there were only three percent fewer deaths caused by diarrhea, according to research from the United Nations. In 2019 alone, there were over 15 million episodes of diarrhea in young children worldwide.
This means children are surviving, but not necessarily thriving—or not necessarily living their healthiest life. The magnitude is huge, but the problem still lacks the recognition and prioritization it urgently requires.
Diarrhea has devastating, lasting implications for children and families
Many studies demonstrate that repeated diarrhea infections, especially within the first two years of life, can cause long-term disability, diminishing a child’s quality of life and potentially causing premature death.
Recurring enteric infections, such as those caused by diarrheal disease, may lead to intestinal inflammation and damage in the gut. Compromised gut health inhibits nutrient absorption in the body. This can lead to malnutrition and lasting health consequences, such as stunted physical growth, impaired cognitive development, and/or increased susceptibility to infections, including diarrheal disease and pneumonia. The better we understand these implications, the better we can make meaningful policy decisions to break the cycle of poor health by using strategies and solutions that work together.
We are saving more lives from diarrhea, but what is the future for kids who grow up sick much of their lives? Once a child developmentally misses an opportunity to grow, you can never fix that.
- Dr. Roma Chilengi, Chief Scientific Officer, Centre for Infectious Disease Research in Zambia (CIDRZ)
DefeatDD Blog
No child’s life should be limited by diarrhea
Diarrhea imposes a devastating burden on communities—not just in terms of deaths and illnesses, but also in terms of finances.
When a young child has multiple episodes of diarrhea, he/she is left vulnerable to other infections, malnutrition, and stunting, which can take a lifelong toll on that child’s ability to grow, thrive, and contribute to society.
- When a child gets sick, he/she may miss school and his/her parents must pay for care, which could amount to a significant portion of that family’s income.
- They may also need to stay home to care for their child or take him/her to the clinic or hospital, losing wages from missed time at work.
- Especially in lower-income countries, the cost of diarrhea can push entire families into poverty, known as “medical impoverishment.”
- Often, when one child gets sick, so do other family members. The impact is bigger than one child.
- Stunting, the end result of long-term developmental deficits that repeated diarrhea can cause, is associated with a 25% reduction in average adult earning potential.
Many families are forced to make the impossible choice
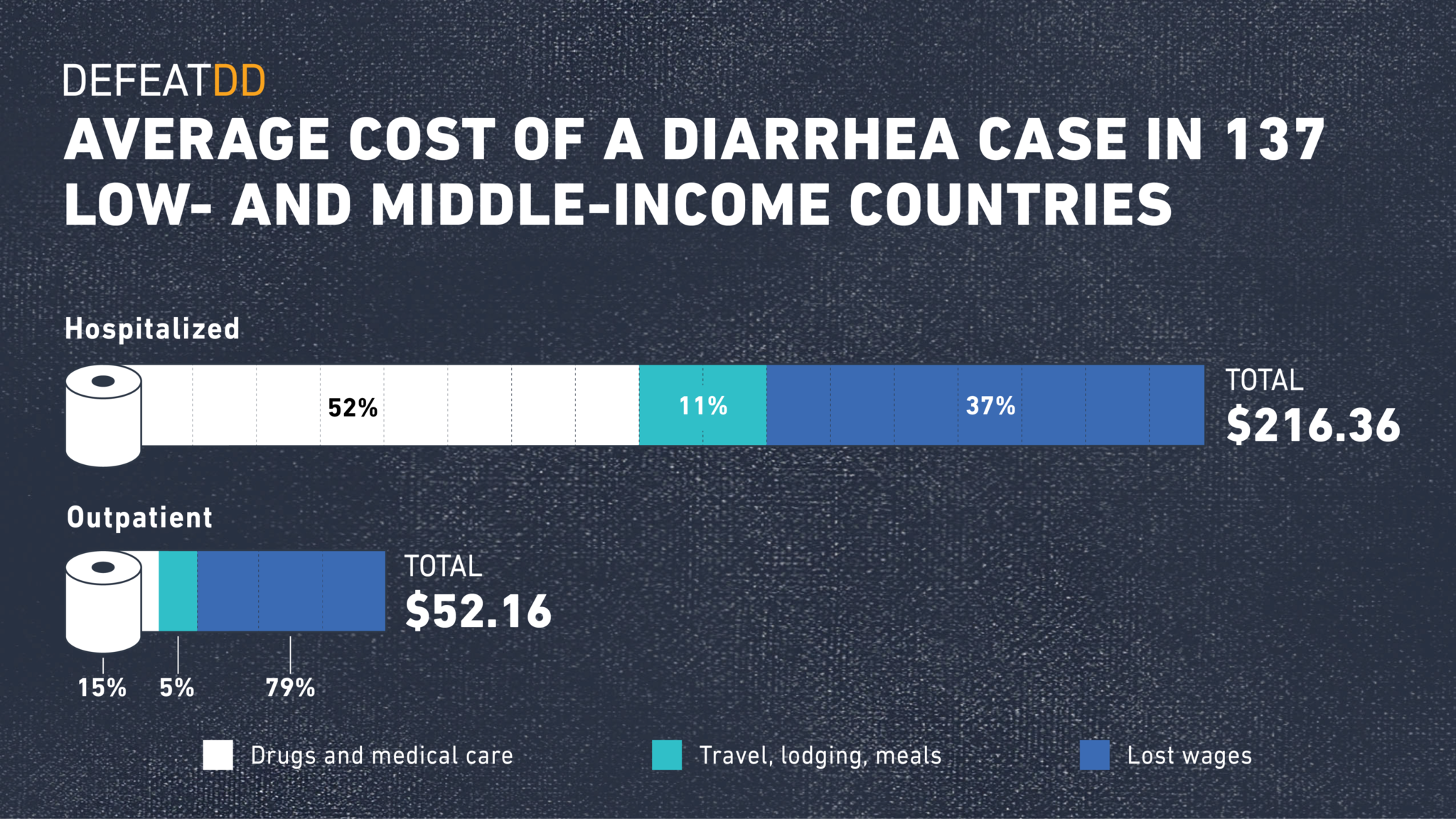
When a children falls ill with diarrheal disease, families often have to chose between treatment and family finances. Treatment costs can cause significant financial strain on households and health care systems alike. A PATH analysis found that, across 137 low- and middle-income countries, modelled costs of childhood diarrhea averaged $52.16 per outpatient episode and $216.36 per inpatient episode, with a significant share of costs due to lost wages and indirect treatment costs like travel and lodging. For many families, including a quarter of those in a Malawi study, these costs are greater than or equal to the entire family’s monthly income. This type of expense can too often push families into poverty.
Take action
Policy decisions are made based on local needs and burden. Find out about diarrhea in your region/country with these resources.
Where to learn more about diarrheal disease
-
Global Burden
WHO/UNICEF
Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality 2000–2015IHME GBD
Global, regional, and national deaths, DALYs, YLDs, YLLs, prevalence, incidence, maternal mortality ratio attributable to diarrheal disease in 2016.– Visualization of GBD estimates
– Raw, downloadable GBD 2019 estimates
– IHME websiteSee also: Global disability-adjusted life year (DALY) estimates of long-term health burden due to diarrheal disease.
Global Enteric Multicenter Study Reanalysis 2016
Causes of diarrheal disease in children
-
National/Regional Burden
WHO/MCEE
Estimates for child causes of death 2000-2015IHME GBD
Global, regional, and national deaths, DALYs, YLDs, YLLs, prevalence, incidence, maternal mortality ratio attributable to diarrheal disease in 2019– Visualization of GBD estimates
– Raw, downloadable GBD 2019 estimates
– IHME websiteCountdown to 2030
(includes coverage levels of health interventions by country to reduce maternal, newborn, and child mortality)WHO/Centers for Diseases Control (CDC)
Global, regional, and national estimates of rotavirus mortality in children 2016WHO/Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group (FERG)
Estimates of the global burden of foodborne diseasesUNICEF
Deaths, treatment sought for diarrhea, treatment administered (ORS and zinc) statistics by countryInternational Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS)
National Family Health Survey, India estimates
Yes, we've made progress, but there's more to be done.
It’ll take focus and prioritization from governments and donors, integrated efforts such as the Integrated Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Pneumonia and Diarrhea (GAPPD), and continued pressure and calls for accountability by advocates.
Continue to SolutionsFurther reading:
- Child Health Spotlights (Pneumonia & Diarrhea).
- Countdown to 2030. A Decade of Tracking Progress for Maternal, Newborn and Child Survival: The 2017 Report.
- DefeatDD infographic. Why is diarrhea dangerous?
- DefeatDD.
- DefeatDD. An impossible choice: the dangerous disruption of diarrhea treatment costs.
- DefeatDD. DefeatDD campaigns.
- DefeatDD. How we measure the true impact of diarrheal disease.
- DefeatDD’s new infographic on gut damage makes environmental enteropathy digestible.
- Demographic and Health Surveys. Child Health.
- Every Woman Every Child Report.
- IHME. Global Burden of Disease.
- IHME. Mapping geographical inequalities in childhood diarrhoeal morbidity and mortality in low-income and middle-income countries, 2000–17: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.
- The Lancet. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000–15: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Thousand Days. The Impact of Poor Sanitation on Nutrition.
- UNICEF/World Health Organization. Ending preventable child deaths from pneumonia and diarrhoea by 2025: The integrated global action plan for pneumonia and diarrhoea (GAPPD).
- UNICEF: Diarrhoea
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals.
- World Health Organization. Diarrhoeal disease.
- World Health Organization. Global Strategy for Women's, Children's and Adolescent's Health 2016-2030.



